Information
EXPORTING TO THE EU
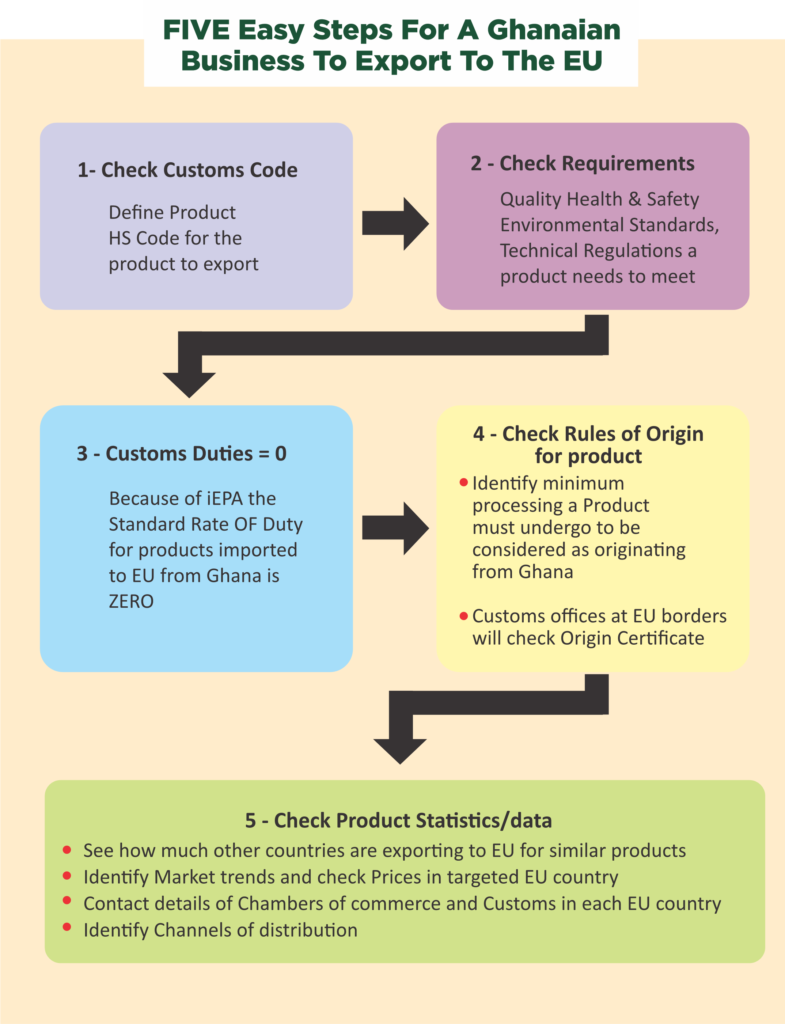
The iEPA allows duty-free quota-free market access for Ghanaian goods into the EU. To enter the EU market, Ghanaian goods must comply with the technical requirements and international standards that prevail in the EU and its member countries
Requirements for exporting to the EU
Enterprises interested in exporting their products to the EU should take into consideration a number of requirements:

Goods classification:
The EU uses the Combined Nomenclature to classify goods; it is mostly based on the Harmonised System (HS) Nomenclature developed within the framework of the World Customs Organisation (WCO).
The EU's Combined Nomenclature is updated every year and is available on the EC website, with explanatory notes.
Documentation:
Most often, the importing side fills out the SAD. Depending on the type of goods, additional documents must be presented to the customs bodies; this includes invoices, certificates of origin, import licences and inspection certificates (such as health, veterinary or plant health certificates) that correspond to the EU's SPS requirements (see below).
SPS requirements:
- General principles: considering general principles and requirements, the reference food law is Regulation (EC) No. 178/2002 ;
- Labelling and packaging: Regulation (EC) No. 1169/2011 provides information on food labelling and packaging. For packaging, the main reference is Regulation (EC) No. 1935/2004; any material in contact with foodstuffs must be safe;
- Animal and plant health: EU Directive 2002/99/EC lays down the animal health rules. The EU Plant Health Directive (2000/29/EC) lays down SPS requirements for plants and plant products;
- Product safety: for most products, legislation is limited to safety and health requirements.
Regulations for specific non-food products include:
- Pharmaceutical products – such imports must be authorised at either the member state or the EU level;
- Chemical products – Regulation EC No. 1907/2006 on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals (REACH) is the EU regulation on chemicals. REACH is relevant to most industrial sectors;
- Biocides – Regulation (EU) No. 528/2012 regulates imports of biocides.
National Requirements:

Information
Sources of information for exporting to the EU
- The EU export helpdesk
Regardless of the exported commodity, all exporters based in Ghana can use the on-line and free access EU export helpdesk to obtain detailed information about EU and national import requirements and procedures using the following website link: http://trade.ec.europa.eu/tradehelp/
The Export Helpdesk online is designed for businesses interested in exporting to the EU. The exporter will find all exporting requirements to the EU, including: health, safety and technical standards to meet customs duties needed to pay at the border internal taxes in each of the 28 EU countries the rules of origin that define where a product is from and whether it profits from preferential duty rates and forms to send with the exporter’s shipments
In order to search for specific information in the website, exporters would need to identify the Harmonised System (HS) product code.
2. Ghana Export Promotion Authority – GEPA
GEPA is the national focal point Agency for the development and promotion of non-traditional exports from Ghana. GEPA has its head office in the Africa Trade House Accra, and has regional offices in Kumasi, Takoradi, Ho, Tamale, Bolgatanga, Koforidua and Cape Coast. The Agency facilitates efforts of exporters and potential exporters in production development and in expansion of their product supply base.
GEPA also assists in market development through the organisation of business-to-business events, trade shows and exhibitions and provides access to trade information through its Impact Hub which is a state-of-the-art Trade Information Centre. Potential exporters who would like to know more about foreign markets (such as the EU) and the related procedures and requirements, can get in touch with GEPA using the following website link https://www.gepaghana.org/.


